Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Fe
-FeSuzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(7), p.075102_1 - 075102_7, 2024/02
Fracture of body centred cubic (bcc) metals and alloys below the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature is brittle. This is theoretically explained by the notion that the critical stress intensity factor of a given crack front for brittle fracture is smaller than that for plasticdeformation; hence, brittle fracture is chosen over plastic deformation. Although this view is true from a macroscopic point of view, such brittle fracture is always accompanied by small-scale plastic deformation in the vicinity of the crack tip, i.e. crack tip plasticity. This short paper investigates the origin of this plasticity using atomistic modeling with a recently developed machine-learning interatomic potential of  -Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
-Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review B, 108(24), p.245110_1 - 245110_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We develop a mean-field theory of a novel Kondo effect emerging in systems without a Fermi surface, which instead emerges under strong magnetic fields. We determine the magnitude of the Kondo condensate, which is a particle pairing composed of conducting Dirac fermions and localized impurities. We focus on the competition between the Kondo effect and the energy gap formation that stems from the pairing among the Dirac fermions leading to the dynamical chiral symmetry breaking. We find that this competition induces a quantum critical point. We also investigate finite-temperature effects. This system at vanishing fermion density can be studied with Monte Carlo lattice simulations, which do not suffer from the sign problem.
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Urata, Shingo*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The first sharp peak diffraction peak (FSDP) in the structure factor of amorphous materials is thought to reflect the medium-range order structure in amorphous materials, and the structural origin of the FSDP has been a subject of ongoing debate. In this study, we employed machine learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) with nearly first-principles calculation accuracy to investigate the structural origin of the FSDP in high-density silica glass. First, we successfully reproduced various experimental data of high-density silica glass using MLMD. Furthermore, we revealed that the development (or reduction) of the FSDP in high-density silica glass is characterized by the deformation behavior of ring structures in Si-O covalent bond networks under compression.
Lee, S.*; Nakata, Koki; Tchernyshyov, O.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184432_1 - 184432_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically investigate the interaction between magnons and a Skyrmion-textured domain wall in a two-dimensional antiferromagnet and elucidate the resultant properties of magnon transport. Using supersymmetric quantum mechanics, we solve the scattering problem of magnons on top of the domain wall and obtain the exact solutions of propagating and bound magnon modes. Then, we find their properties of reflection and refraction in the Skyrmion-textured domain wall, where magnons experience an emergent magnetic field due to its non-trivial spin texture-induced effective gauge field. Finally, we show that the thermal transport decreases as the domain wall's chirality increases. Our results suggest that the thermal transport of an antiferromagnet is tunable by modulating the Skyrmion charge density of the domain wall.
Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 107(7), p.074015_1 - 074015_15, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.75(Astronomy & Astrophysics)A chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated, which is based on 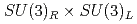 chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the
chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the 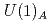 and flavor
and flavor 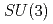 symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons
symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons 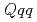 (
(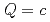 ,
,  and
and 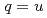 ,
,  ,
,  ), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 276, p.01015_1 - 01015_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We investigate the QCD phase diagram in strong magnetic fields with heavy-quark impurities and determine the ground state within the mean-field analysis. The ground state is characterized by magnitudes of the pairing not only between the light quark and antiquark, i.e., chiral condensate, but also between the light quark and heavy-quark impurity, dubbed the Kondo condensate. We propose signatures of the interplay and/or competition between those two pairing phenomena reflected in the magnitude of the chiral condensate that is saturated with respect to the magnetic-field strength and anomalously increases with increasing temperature.
Massey, D.*; Williams, C. D.*; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Aoyagi, Noboru; Ueda, Yuki; Antonio, M. R.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 127(9), p.2052 - 2065, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Materia, 62(3), p.175 - 181, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi*; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Li, Y.
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-006, 221 Pages, 2023/02
As a part of the structural integrity assessment research for aging light water reactor (LWR) components, a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR) has been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The PASCAL code can evaluate failure probabilities and failure frequencies of core region in reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transients by considering the uncertainties of influential parameters. The continuous development of the code aims to improve the reliability by introducing the analysis methodologies and functions base on the state-of-the-art knowledge in fracture mechanics and domestic data. In the first version of PASCAL, which was released in FY2000, the basic framework was developed for analyzing failure probabilities considering pressurized thermal shock events for RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs). In PASCAL Ver. 2 released in FY 2006, analysis functions including the evaluation methods for embedded cracks and crack detection probability models for inspection were introduced. In PASCAL Ver. 3 released in FY 2010, functions considering weld-overlay cladding on the inner surface of RPV were introduced. In PASCAL Ver. 4 released in FY 2017, we improved several functions such as the stress intensity factor solutions, probabilistic fracture toughness evaluation models, and confidence level evaluation function by considering epistemic and aleatory uncertainties related to influential parameters. In addition, the probabilistic calculation method was also improved to speed up the failure probability calculations. To strengthen the practical applications of PFM methodology in Japan, PASCAL code has been improved since FY 2018 to enable PFM analyses of RPVs subjected to a broad range of transients corresponding to both PWRs and boiling water reactors, including pressurized thermal shock, low-temperature over pressure, and normal operational transients. In particular, the stress intensi
Yabuuchi, Kiyohiro*; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 574, p.154161_1 - 154161_6, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In nuclear materials, irradiation defects cause degradation of mechanical properties. In these materials, the relationship between dislocations and voids is particularly important for mechanical strength. Although only spherical voids have been studied in the past, this study focuses on faceted voids, which are observed simultaneously with spherical voids. In the current study, molecular dynamics was used to analyze the effect of faceted voids in the irradiation hardening of pure iron. Specifically, we clarified the difference in obstacle strength and interaction processes between spherical voids and faceted voids, and that even faceted voids show differences in interaction depending on their crystallographic arrangement with dislocations.
 - and K-montmorillonite
- and K-montmorilloniteKawakita, Ryohei; Saito, Akito*; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Otake, Tsubasa*; Sato, Tsutomu*
Applied Clay Science, 231, p.106722_1 - 106722_7, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:21.06(Chemistry, Physical)Tsugawa, Kiyoto*; Hayakawa, Sho*; Okita, Taira*; Aichi, Masaatsu*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 215, p.111806_1 - 111806_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 29(2), p.63 - 81, 2022/12
The understanding of the swelling phenomenon of montmorillonite is essential to predict the physical and chemical behavior of clay-based barriers in radioactive waste disposal systems. This study investigated the key factors controlling crystalline swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. On the basis of the comparisons between MD simulated and experimental results, the water content in the interlayer in five homoionic (Na , K
, K , Cs
, Cs , Ca
, Ca and Sr
and Sr ) montmorillonite was strongly correlated to the hydration number and the preference of an outer- or inner-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The detailed analysis for these results offer insights that the hydration number is controlled by the hydration free energy, the volume and the distribution of each interlayer counter-ion. The systematic MD simulations with virtually variable parameters clarified that the hydration free energy and the charge of interlayer counter- ions compete as influencing factors, and the control the formation rate of an outer-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The empirical relationships between these key factors will allow essential insights into predicting the swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions.
) montmorillonite was strongly correlated to the hydration number and the preference of an outer- or inner-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The detailed analysis for these results offer insights that the hydration number is controlled by the hydration free energy, the volume and the distribution of each interlayer counter-ion. The systematic MD simulations with virtually variable parameters clarified that the hydration free energy and the charge of interlayer counter- ions compete as influencing factors, and the control the formation rate of an outer-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The empirical relationships between these key factors will allow essential insights into predicting the swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.19701_1 - 19701_10, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:41.53(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Body-centered-cubic (bcc) transition metals, such as  -Fe and W, cleave along the {100} plane, even though the surface energy is the lowest along the {110} plane. To unravel the mechanism of this odd response, large-scale atomistic simulations of curved cleavage cracks of
-Fe and W, cleave along the {100} plane, even though the surface energy is the lowest along the {110} plane. To unravel the mechanism of this odd response, large-scale atomistic simulations of curved cleavage cracks of  -Fe were conducted in association with stress intensity factor analyses of straight crack fronts using an interatomic potential created by an artificial neural network technique. The study provides novel findings: Dislocations are emitted from the crack fronts along the {110} cleavage plane, and this phenomenon explains why the {100} plane can be the cleavage plane. However, the simple straight crack-front analyses did not yield the same conclusion. It is suggested that atomistic modeling, at sufficiently large scales to capture the inherent complexities of materials using highly accurate potentials, is necessary to correctly predict the mechanical strength. The method adopted in this study is generally applicable to the cleavage problem of bcc transition metals and alloys.
-Fe were conducted in association with stress intensity factor analyses of straight crack fronts using an interatomic potential created by an artificial neural network technique. The study provides novel findings: Dislocations are emitted from the crack fronts along the {110} cleavage plane, and this phenomenon explains why the {100} plane can be the cleavage plane. However, the simple straight crack-front analyses did not yield the same conclusion. It is suggested that atomistic modeling, at sufficiently large scales to capture the inherent complexities of materials using highly accurate potentials, is necessary to correctly predict the mechanical strength. The method adopted in this study is generally applicable to the cleavage problem of bcc transition metals and alloys.
Kobayashi, Keita; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Applied Clay Science, 228, p.106596_1 - 106596_11, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:77.65(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Cooper, M. W. D.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.9808_1 - 9808_11, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:71.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Sasa, Narimasa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054001_1 - 054001_8, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary) TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloy
TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloyChen, J.*; Yoshida, Kenta*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Shimada, Yusuke*; Inoue, Koji*; Konno, Toyohiko*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Materials Transactions, 63(4), p.468 - 474, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In situ electron irradiation using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) was performed to visualize the Frank loop evolution in aluminium-copper (Al-Cu) alloy with an atomic-scale spatial resolution of 0.12 nm. The  HRTEM observation along the [110] direction of the FCC-Al lattice, Frank partial dislocation bounding an intrinsic stacking fault exhibited an asymmetrical climb along the
HRTEM observation along the [110] direction of the FCC-Al lattice, Frank partial dislocation bounding an intrinsic stacking fault exhibited an asymmetrical climb along the  112
112 direction opposed to those in the reference pure Al under an electron irradiation, with a corresponding displacement-per-atom rate of 0.055-0.120 dpa/s. The asymmetrical climb of the partial dislocation was described as pinning effects due to Cu-Cu bonding in Guinier-Preston zones by a molecular dynamics simulation.
direction opposed to those in the reference pure Al under an electron irradiation, with a corresponding displacement-per-atom rate of 0.055-0.120 dpa/s. The asymmetrical climb of the partial dislocation was described as pinning effects due to Cu-Cu bonding in Guinier-Preston zones by a molecular dynamics simulation.
 3(111) and
3(111) and  5(0-13) grain boundaries of
5(0-13) grain boundaries of  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Metals, 12(4), p.662_1 - 662_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus atoms in steels accumulate at grain boundaries via thermal and/or irradiation effects and induce grain boundary embrittlement. Quantitative prediction of phosphorus segregation at grain boundaries under various temperature and irradiation conditions is therefore essential for preventing embrittlement. To develop a model of grain boundary phosphorus segregation in  -iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries (
-iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries ( 3[1-10](111) and
3[1-10](111) and  5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the
5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the  3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the
3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the  5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Araki, Yasufumi; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074028_1 - 074028_19, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.77(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose a new mechanism of the heavy-quark spin polarization (HQSP) in quark matter induced by the Kondo effect under an external magnetic field. The Kondo effect is caused by a condensate between a heavy and a light quark called the Kondo condensate leading to a mixing of the heavy- and light-quark spins. Thus, the HQSP is driven through the Kondo effect from light quarks coupling with the magnetic field in quark matter. For demonstration, we employ the Nambu-Jona-Lasinio type model under a magnetic field and investigate the HQSP within the linear response theory with vertex corrections required by the 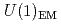 electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.
electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.